Blog
Sprouted seeds as a living food system are seeds that have begun germination and transformed into young, metabolically active plants. Unlike raw or unsprouted seeds, sprouted seeds are living foods that provide enhanced digestibility, nutrient bioavailability, and enzymatic activity. During sprouting, complex compounds in seeds break down naturally, reducing antinutrients like phytic acid and lectins, which allows the body to absorb minerals, vitamins, and essential amino acids more efficiently. This makes sprouted seeds a foundational component of a living food system, providing natural energy, antioxidant protection, and bioactive compounds that support overall health.

The significance of sprouted seeds as a living food system extends beyond nutrition. They represent a sustainable, regenerative approach to food that aligns with biohacking principles and functional nutrition. Sprouts are easy to incorporate into diets—whether in salads, smoothies, or grain bowls—and their living nature ensures they deliver maximum health benefits in a concentrated, digestible form. For anyone focused on holistic wellness, gut health, and nutrient-dense foods, sprouted seeds provide an accessible, versatile, and environmentally friendly solution.
Key benefits of sprouted seeds include:
- Enhanced nutrient absorption and enzymatic activity
- Rich source of vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants
- Supports a regenerative and living food system
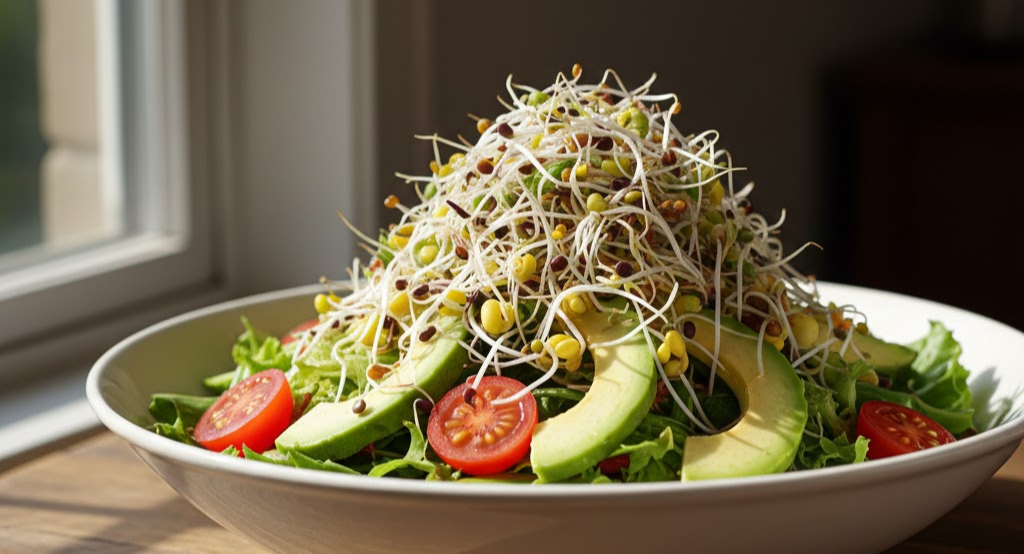

Nutritional Profile of Sprouted Seeds
Sprouted seeds as a living food system are among the most nutrient-dense foods available. The germination process activates enzymes that enhance vitamin content, including vitamin C, B-complex vitamins, and carotenoids, while partially breaking down proteins into amino acids for easier digestion. This makes sprouted seeds ideal for anyone seeking high-quality plant-based nutrition. In addition to vitamins, sprouted seeds are loaded with essential minerals like calcium, magnesium, and iron, which are more bioavailable compared to unsprouted seeds. The enzymatic activity during sprouting is central to their living food system benefits, ensuring that every bite delivers maximum nutrient density and digestive ease.
Beyond traditional nutrients, sprouted seeds are rich in phytonutrients, flavonoids, and phenolic acids, which promote antioxidant defense, reduce oxidative stress, and support cellular function. Consuming sprouted seeds regularly improves metabolic efficiency, supports the immune system, and maintains energy levels throughout the day. For biohackers, athletes, and health-conscious individuals, integrating sprouted seeds as a living food system can significantly improve nutrient intake without reliance on supplements. Their combination of enzyme activation, mineral accessibility, and antioxidant power makes sprouted seeds a cornerstone of functional nutrition.

How Sprouting Enhances Digestive Health
Sprouted seeds as a living food system naturally support digestive health. The sprouting process breaks down complex carbohydrates and proteins into simpler molecules, making them easier for the digestive system to process. Enzymes like amylase, protease, and lipase are activated during sprouting, aiding in the breakdown of starches, proteins, and fats. This enzymatic activity not only improves nutrient absorption but also reduces digestive discomfort, such as bloating or gas, which can occur with raw seeds or legumes.
Sprouted seeds also contain prebiotic fibers that nourish beneficial gut bacteria, improving microbiome health and promoting efficient digestion. Regular consumption of sprouted seeds can help maintain a healthy gut lining, regulate bowel movements, and enhance overall nutrient uptake. For individuals seeking functional foods and biohacking strategies, sprouted seeds provide a living, nutrient-rich, and enzyme-activated food system that supports gut health, metabolic function, and long-term wellness. Their inclusion in daily meals ensures the digestive system works efficiently while benefiting from living nutrition.
Digestive advantages include:
- Enhanced enzymatic support for protein and carbohydrate breakdown
- Prebiotic fibers supporting a healthy gut microbiome
- Improved nutrient absorption and reduced digestive discomfort
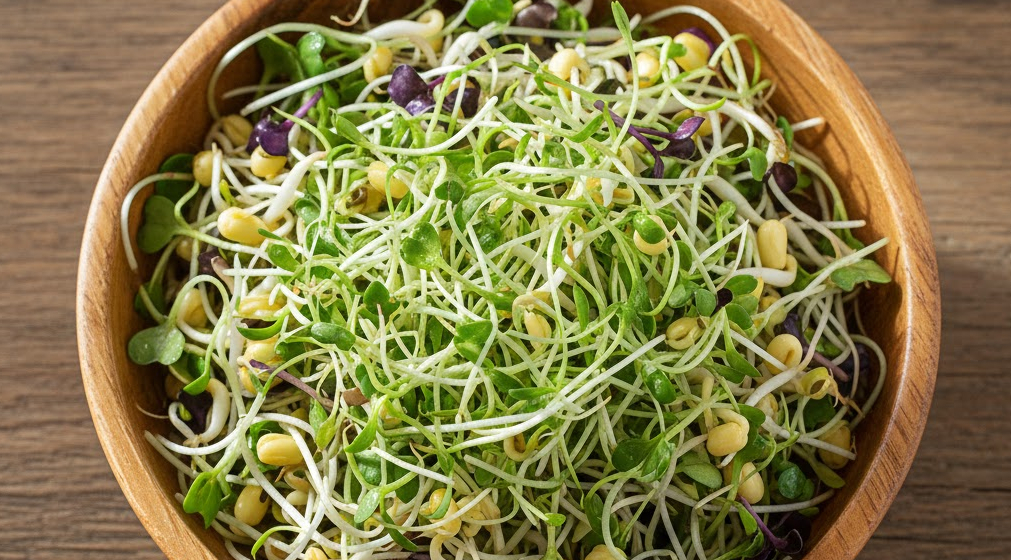

Common Types of Sprouted Seeds
Several types of seeds are widely used in sprouted seeds as a living food system, each offering unique nutritional and culinary benefits. Alfalfa sprouts are mild-tasting and high in vitamin K, supporting bone health. Mung bean sprouts are rich in plant-based protein and essential amino acids, making them ideal for high-protein meals. Broccoli sprouts are renowned for sulforaphane content, a powerful antioxidant with anti-inflammatory properties. Additional options like sunflower, radish, and lentil sprouts provide variety in taste, texture, and nutritional profiles, making sprouted seeds a versatile ingredient for any living food system.
Sprouted seeds can be easily incorporated into meals or grown at home. Their fast growth, often within 3–7 days, provides a continuous supply of fresh, living foods without reliance on industrial farming. This accessibility allows individuals to maintain a sustainable, nutrient-dense diet, ensuring they consume a wide range of vitamins, minerals, enzymes, and antioxidants daily. For biohackers and wellness enthusiasts, selecting the right sprouted seed enhances both flavor and health impact.

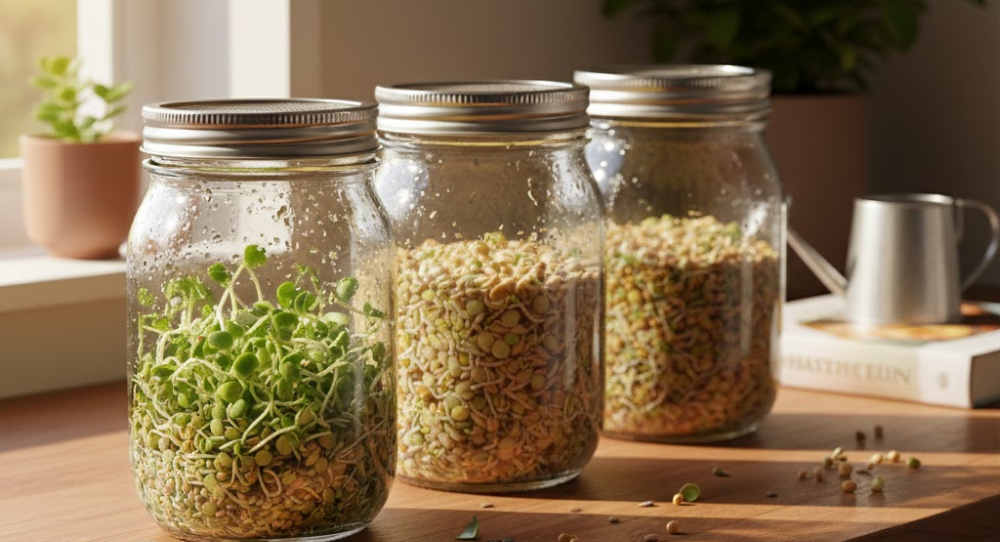
How to Grow Sprouted Seeds at Home
Growing sprouted seeds as a living food system at home is simple, cost-effective, and requires minimal equipment. A clean glass jar, a breathable mesh lid or cloth, and filtered water are sufficient to start sprouting. Seeds are soaked for 6–12 hours to activate germination, then rinsed and drained twice daily to maintain moisture and prevent mold growth. Within 3–7 days, sprouts are ready for consumption, delivering peak enzyme activity, nutrient density, and living food benefits.
Home sprouting not only ensures fresh, clean, and nutrient-rich sprouts but also creates a direct connection to a living food system. Observing seeds germinate provides insight into plant biology, food cycles, and natural nutrition. This makes sprouted seeds a mindful, functional, and sustainable food choice for daily consumption. With proper care, home sprouts offer continuous, renewable nutrition, supporting digestive health, immune function, and overall vitality.
Steps for home sprouting:
- Soak seeds in filtered water for 6–12 hours to start germination
- Rinse and drain twice daily to maintain moisture and prevent mold
- Harvest fresh sprouts and store in a clean, cool environment

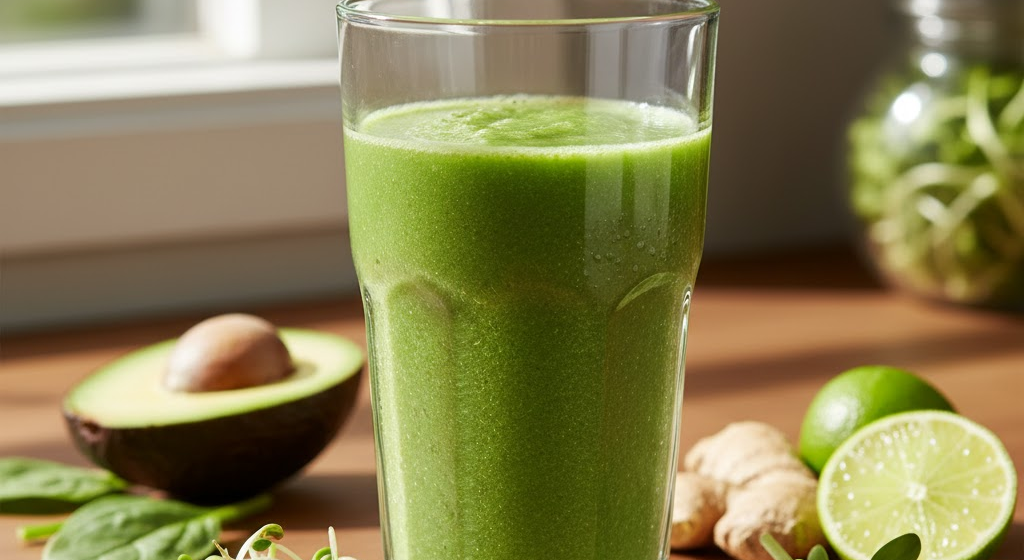
Culinary Uses and Meal Integration
Sprouted seeds as a living food system are not only nutrient-dense but also incredibly versatile, making them easy to incorporate into almost any meal. Their fresh, crisp texture, mild or nutty flavors, and living enzymes allow them to complement a wide range of foods. In salads, sprouted seeds can replace or enhance traditional greens, adding an extra boost of vitamins, minerals, and prebiotic fibers. For example, alfalfa sprouts mixed with spinach, cherry tomatoes, and avocado create a crunchy, nutrient-packed salad that supports digestion and provides antioxidant protection. Mung bean or lentil sprouts add protein and texture, transforming a simple bowl into a complete, living food system meal.
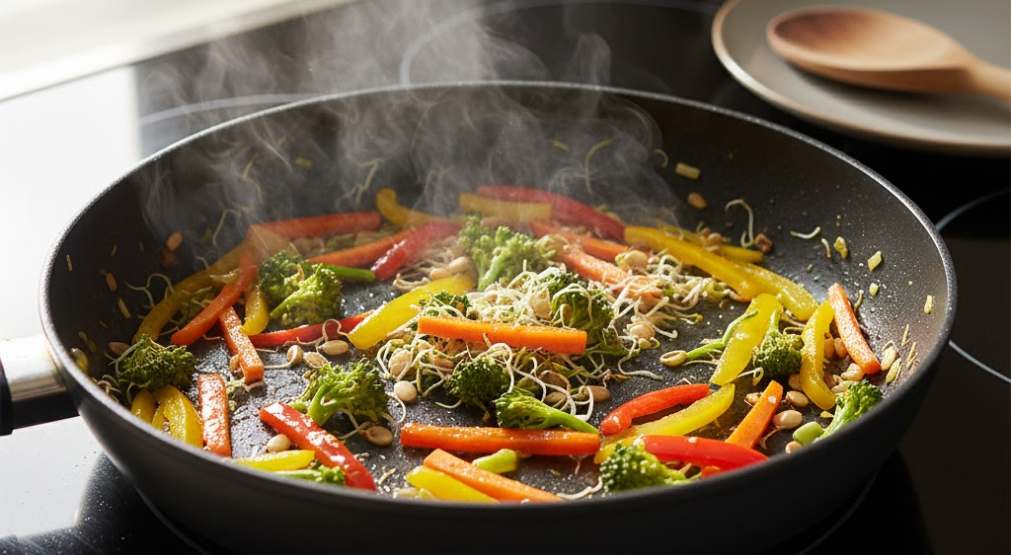
Sprouts are also ideal for smoothies and juices. By blending broccoli sprouts, sunflower sprouts, or radish sprouts into green smoothies, individuals can harness the enzymatic activity and phytonutrients of sprouted seeds without altering taste significantly. This is particularly useful for people looking to integrate sprouted seeds as a living food system seamlessly into busy lifestyles. Lightly cooking sprouts is another option; sautéed sprouts retain much of their nutrient content while adding flavor and texture to stir-fries, grain bowls, or noodle dishes. Combining sprouts with grains, fermented foods like kimchi or sauerkraut, and seeds or nuts enhances both taste and health benefits, creating a holistic meal that supports energy, mental clarity, and immune function.
In addition to daily meals, sprouted seeds can be used in snacks and creative culinary applications. For instance, topping sandwiches, avocado toast, or hummus bowls with fresh sprouts introduces living nutrition and enzymatic benefits to every bite. They can also be incorporated into baked goods such as sprouted seed bread or crackers, although minimal cooking preserves the highest nutrient content. For biohackers, health enthusiasts, or anyone pursuing functional nutrition, integrating sprouted seeds as a living food system into meals ensures consistent intake of vitamins, minerals, antioxidants, and digestive enzymes. With their versatility, sprouted seeds elevate both everyday meals and gourmet creations, making a nutrient-dense, living food system accessible, practical, and delicious.

Final Thoughts on “Sprouted Seeds as a Living Food System”
Sprouted seeds as a living food system represent one of the most accessible, nutrient-dense, and sustainable ways to enhance modern diets. By transforming simple seeds into living, enzymatically active foods, sprouting unlocks vitamins, minerals, antioxidants, and amino acids in forms that the body can absorb easily. This makes sprouted seeds not just a food choice, but a living food system that supports digestion, immune function, energy metabolism, and overall wellness. Whether consumed raw, blended into smoothies, or lightly cooked in meals, sprouts provide a constant source of living nutrition that integrates seamlessly into daily life.
Beyond their nutritional benefits, sprouted seeds offer a sustainable and environmentally friendly approach to food. They require minimal resources, grow quickly, and generate almost no waste, making them a cornerstone of eco-conscious diets. Cultivating sprouts at home empowers individuals to take control of their food supply while engaging directly with the natural cycles of growth and nourishment. This practical, regenerative approach aligns perfectly with biohacking strategies and functional nutrition goals, emphasizing both personal health and ecological responsibility.
Integrating sprouted seeds as a living food system into meals encourages creativity and variety. From fresh salads and wraps to smoothies, stir-fries, and grain bowls, sprouts enhance taste, texture, and nutritional impact. Regular consumption ensures consistent intake of enzymes, prebiotic fibers, and phytonutrients, supporting long-term digestive health, mental clarity, and vitality.
In summary, sprouted seeds are more than a food—they are a living, dynamic, and regenerative system that transforms everyday meals into functional, nutrient-rich experiences. For anyone committed to holistic wellness, sustainable eating, and optimal nutrition, embracing sprouted seeds as a living food system is a simple, practical, and highly effective choice.