Blog
Aging brings noticeable changes to our bodies, and one of the most significant is the gradual loss of muscle mass, which begins around the age of 40. Preserving strength and mobility is critical not only for aesthetics but also for overall health and independence.
One of the most effective tools in this battle is proper protein intake, which ensures that muscles receive the building blocks they need for repair and growth. Understanding Protein after 40: how to maintain muscles and health is vital for anyone looking to stay fit, maintain energy, and reduce the risk of age-related diseases. By combining the right amount of protein with regular exercise, individuals over 40 can counteract muscle loss, support recovery, and improve longevity.
Moreover, protein supports more than just muscle growth. It stabilizes blood sugar, improves satiety, and aids in maintaining a healthy metabolism, which naturally slows with age. Knowing Protein after 40: how to maintain muscles and health allows for smart dietary choices that complement daily activity and resistance training routines. Incorporating high-quality protein sources such as lean meats, dairy, eggs, and plant-based alternatives ensures that your body has what it needs to thrive while keeping fat gain in check. Establishing this habit early can make a significant difference in physical performance and overall well-being.
Tips for protein after 40:
- Prioritize high-quality protein from eggs, fish, lean meats, and legumes.
- Distribute protein evenly across meals for optimal absorption.
- Pair protein with carbohydrates and healthy fats for energy and recovery.

Exercise and Protein Synergy
Protein after 40: how to maintain muscles and health is most effective when paired with regular exercise, particularly strength training. Resistance exercises stimulate muscle protein synthesis, increase bone density, improve joint stability, and elevate metabolism. Compound movements like squats, deadlifts, push-ups, and rows engage multiple muscles simultaneously, enhancing overall strength and functional fitness. Cardiovascular exercises, yoga, and stretching complement resistance training by improving heart health, flexibility, and balance, lowering the risk of injuries. Post-workout protein intake accelerates recovery, reduces muscle soreness, and prepares muscles for future workouts, maximizing the benefits of both exercise and nutrition.
Consistency is critical: aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity cardio weekly, combined with two to three strength sessions targeting major muscle groups. Recovery strategies such as proper sleep, stretching, and hydration amplify the effects of protein and training. Adults over 40 can preserve lean mass, boost metabolism, and maintain functional capacity by integrating structured exercise with adequate protein consumption. This combination is the cornerstone of healthy aging.
Exercise and protein tips:
- Include resistance training for all major muscle groups.
- Incorporate cardio and flexibility exercises for overall fitness.
- Consume protein within 30–60 minutes after workouts.

Types of Protein for Adults Over 40
Protein after 40: how to maintain muscles and health requires choosing the right types of protein for absorption, digestibility, and nutrient profile. Animal-based proteins such as chicken, fish, eggs, and dairy provide complete amino acid profiles and are highly bioavailable. Plant-based proteins like legumes, quinoa, soy, and nuts offer essential nutrients and fiber, supporting heart health and digestion. Combining various protein sources ensures all essential amino acids are consumed, maintaining muscle mass and metabolic health. For those with dietary restrictions, protein powders from whey, pea, or rice can fill nutritional gaps efficiently.
Timing and portion size matter: aim for 20–40 grams of protein per meal to stimulate muscle protein synthesis effectively. Pairing protein with other nutrients like omega-3s, antioxidants, and vitamins enhances muscle recovery, joint health, and overall well-being. By selecting a mix of protein sources and planning meals thoughtfully, adults over 40 can sustain muscle mass, improve energy, and prevent age-related muscle decline.
Protein source tips:
- Include a mix of animal and plant-based proteins.
- Use protein powders to supplement gaps.
- Pair protein with nutrient-rich foods for overall health.

Meal Timing and Distribution
Protein after 40: how to maintain muscles and health is optimized when intake is distributed evenly throughout the day. Research shows that spreading protein across 3–5 meals enhances muscle protein synthesis more effectively than consuming a large amount in a single meal. Breakfast, lunch, and dinner should each include adequate protein, with snacks supplemented as needed. Consistent protein intake supports metabolism, stabilizes blood sugar, and reduces muscle breakdown. Meal timing also plays a role in energy levels, helping adults maintain stamina for daily activities, workouts, and cognitive function.
For active adults, pre- and post-workout protein intake maximizes recovery and muscle growth. Incorporating protein-rich snacks such as Greek yogurt, nuts, or boiled eggs between meals ensures continuous amino acid availability. By tracking intake and structuring meals appropriately, adults over 40 can prevent muscle loss, maintain metabolic efficiency, and support overall health effectively.
Meal timing tips:
- Spread protein evenly across 3–5 meals.
- Include protein-rich snacks for sustained energy.
- Time protein intake around workouts for recovery.
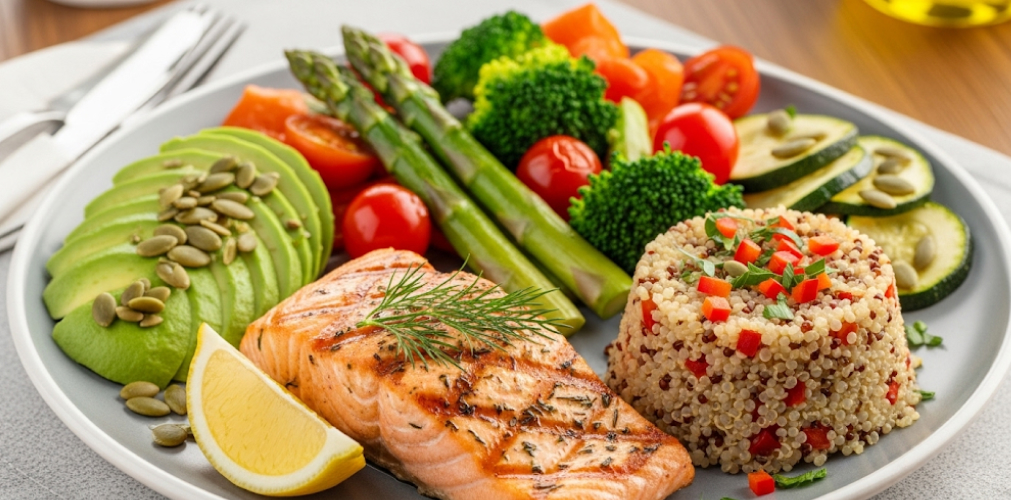

Strength Training Essentials
Protein after 40: how to maintain muscles and health works hand-in-hand with strength training, which preserves muscle mass, supports bone health, and improves metabolic rate. Resistance exercises, such as weightlifting, resistance bands, or bodyweight movements, stimulate muscle growth and enhance functional fitness. Progressive overload ensures that muscles continue to adapt, maintaining strength and preventing age-related decline. Strength training also improves balance, coordination, and joint stability, reducing the risk of falls and injuries.
Consistency and variety are key: target major muscle groups 2–3 times per week, alternating between upper and lower body exercises. Integrating strength training with cardiovascular workouts supports overall heart health and endurance. Adequate protein intake before and after training ensures optimal muscle repair and growth. By committing to regular resistance exercise, adults over 40 can maintain strength, mobility, and independence as they age.
Strength training tips:
- Perform resistance exercises for all major muscle groups.
- Progressively increase intensity to challenge muscles.
- Pair with protein intake for recovery and growth.

Cardiovascular Fitness and Protein
Maintaining cardiovascular fitness is just as important as preserving muscle mass after 40. As the heart and blood vessels age, aerobic capacity naturally declines, making regular cardio exercise essential to maintain heart health, stamina, and overall wellness. Combining cardiovascular activity with proper protein intake supports not only muscle preservation but also recovery from higher-intensity workouts. Protein after 40: how to maintain muscles and health plays a crucial role in repairing small muscle tears that can occur during cardio sessions, ensuring that both muscles and joints remain strong and resilient. By integrating protein-rich meals with aerobic exercise, the body can sustain energy levels, reduce fatigue, and improve overall exercise performance, which is vital for maintaining an active lifestyle.
Furthermore, cardiovascular training enhances metabolic efficiency and promotes a healthy weight, complementing the muscle-supportive effects of protein. Adequate protein intake aids in preserving lean muscle during periods of calorie control or weight management, which often accompanies cardio programs. Incorporating Protein after 40: how to maintain muscles and health into post-exercise nutrition routines maximizes the benefits of both aerobic and resistance training, ensuring muscles recover properly and cardiovascular health remains optimal. Maintaining this balance between cardio and protein consumption helps prevent age-related muscle decline while improving endurance, energy levels, and overall vitality.
Cardio and protein tips:
- Include 150 minutes of moderate-intensity cardio weekly.
- Combine cardio with strength training for optimal body composition.
- Maintain protein intake around exercise to prevent muscle loss.

Recovery and Protein
Recovery is a critical component of maintaining muscle mass and overall health, especially as we age. After 40, the body’s ability to repair muscle tissue and recover from physical exertion naturally slows down, making Protein after 40: how to maintain muscles and health even more essential. Consuming protein immediately after exercise helps stimulate muscle protein synthesis, reduces soreness, and accelerates repair. High-quality sources such as lean meats, fish, eggs, dairy, and plant-based proteins provide essential amino acids that the body cannot produce on its own, making them indispensable for recovery. Alongside protein intake, ensuring proper hydration, sleep, and rest days contributes significantly to maintaining strength, mobility, and energy levels.
Additionally, spreading protein consumption evenly throughout the day enhances its benefits. Multiple small protein-rich meals or snacks ensure a continuous supply of amino acids for muscle repair and maintenance, supporting metabolic function and energy balance. Resistance training combined with adequate post-workout protein intake maximizes muscle retention, which is crucial in counteracting age-related muscle loss. Incorporating Protein after 40: how to maintain muscles and health principles into daily routines ensures that recovery is optimized, helping individuals maintain physical performance and overall wellness. A consistent focus on recovery and protein can profoundly impact long-term health, vitality, and the ability to stay active well into later decades.
Recovery tips:
- Prioritize 7–9 hours of sleep per night.
- Include active recovery like stretching or light walking.
- Consume protein consistently during recovery periods.

Final Thoughts
Maintaining muscle mass and overall wellness as we age requires intentional effort, especially after 40. Protein after 40: how to maintain muscles and health becomes a central factor in counteracting the natural decline in muscle mass and metabolism that occurs with aging. Ensuring that every meal contains high-quality protein sources—such as lean meats, fish, eggs, dairy, legumes, and plant-based alternatives—is essential for muscle repair, recovery, and sustained energy.
Resistance training, combined with sufficient protein intake, helps preserve strength, improve posture, and enhance balance, which are all critical for daily function and independence. Additionally, incorporating protein-rich snacks between meals can prevent muscle breakdown and maintain steady energy levels throughout the day. Making conscious nutritional choices, alongside regular physical activity, sets the foundation for long-term health and vitality.
Beyond diet, lifestyle factors greatly influence the effectiveness of Protein after 40: how to maintain muscles and health strategies. Sleep, hydration, and stress management all play crucial roles in muscle recovery and nutrient utilization. Consuming protein around workouts amplifies its benefits, promoting optimal muscle protein synthesis and reducing the risk of injury.
A balanced exercise regimen—including strength training, cardio, and flexibility exercises—supports muscle retention while enhancing cardiovascular health and joint function. Small, consistent adjustments, such as replacing low-protein snacks with Greek yogurt, cottage cheese, or protein shakes, can have a significant impact over time. Tracking protein intake and aligning it with physical activity ensures the body gets what it needs for growth and repair. This approach allows individuals over 40 to maintain strength, improve metabolism, and support overall wellness more effectively.
Finally, a structured, long-term plan is key to mastering Protein after 40: how to maintain muscles and health. Combining exercise, nutrition, and proper recovery fosters a sustainable approach to aging well. Prioritizing protein-rich meals after workouts accelerates recovery and maintains muscle mass. Diversifying protein sources not only provides essential amino acids but also supports bone health, immune function, and metabolic efficiency. Additionally, staying informed about meal planning, supplementation options, and evidence-based strategies helps maximize results. By embracing these principles, anyone over 40 can significantly improve strength, vitality, and quality of life. In summary, focusing on Protein after 40: how to maintain muscles and health consistently, alongside balanced exercise and recovery, ensures long-term fitness, muscle preservation, and well-being.
Key takeaways:
- Include high-quality protein in every meal and snack.
- Pair resistance training with protein intake for optimal muscle preservation.
- Maintain balanced lifestyle habits—sleep, hydration, and stress management.