Blog
Stress, whether physical or emotional, is an undeniable part of modern life. It triggers a cascade of biochemical reactions within the body, significantly influencing nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD+), a crucial coenzyme vital for energy metabolism and cellular health. Understanding the impact of stress on NAD+ levels is paramount for developing effective strategies to maintain optimal NAD+ and overall well-being.
Under stress, the body activates the sympathetic nervous system, releasing hormones like cortisol. Elevated cortisol increases NAD+ consumption by PARP enzymes, which are involved in DNA repair, a process heightened by stress-induced DNA damage. Chronic stress also impairs mitochondrial function. Mitochondria are the cell’s powerhouses, where NAD+ is essential for adenosine triphosphate (ATP) production. This highlights the impact of stress on NAD+ levels at a fundamental cellular level.
- Stress activates PARP enzymes, consuming NAD+ for DNA repair.
- Cortisol accelerates NAD+ depletion.
- Chronic stress reduces mitochondrial efficiency, affecting NAD+-dependent energy production.

The Role of NAD+ in Cellular Processes and Its Vulnerability to Stress
NAD+ is fundamental for cellular life and health, participating in hundreds of metabolic reactions. It is essential for the Krebs cycle and the electron transport chain, where it contributes to ATP generation. Furthermore, NAD+ is a critical substrate for enzymes like sirtuins, which regulate cellular aging, metabolism, and inflammation, and CD38, involved in immune function. The impact of stress on NAD+ levels directly affects these vital processes.
When the body experiences stress, the increased activity of enzymes like PARP and CD38 leads to heightened NAD+ consumption. This creates an imbalance between NAD+ production and utilization, ultimately lowering its levels. Low NAD+ has far-reaching consequences: it can impair energy metabolism, reduce DNA repair efficiency, worsen mitochondrial function, and compromise sirtuin activity. This contributes to accelerated cellular aging, diminished resilience to damage, and the development of various stress-related diseases. Understanding the impact of stress on NAD+ levels helps us recognize these broader health implications.
- Increased PARP and CD38 activity during stress depletes NAD+.
- NAD+ is essential for cellular energy production.
- NAD+ is a key substrate for sirtuins, regulating cellular aging.

Strategies to Protect NAD+ from Stress: Stress Reduction
One of the most direct ways to mitigate the impact of stress on NAD+ levels is by actively reducing stress itself. While complete avoidance of stress in modern life is unrealistic, effective management strategies exist. The first step involves identifying primary stress sources, whether work-related, personal, or financial. Recognizing these triggers allows for targeted approaches to manage or eliminate them, thereby lessening the impact of stress on NAD+ levels.
Effective stress reduction methods include meditation, yoga, breathing exercises, and mindfulness. Meditation helps focus on the present, reducing anxious thoughts. Yoga combines physical postures with breathing techniques, promoting mind-body relaxation. Deep diaphragmatic breathing can instantly lower stress by activating the parasympathetic nervous system. Mindfulness teaches acceptance of current experiences, reducing their stressful impact. Regular application of these techniques not only lowers current stress but also boosts overall resilience, indirectly safeguarding NAD+ reserves and diminishing the impact of stress on NAD+ levels.
- Cultivate mindfulness to better manage stress responses.
- Identify and minimize major stressors in daily life.
- Regularly practice relaxation techniques like meditation, yoga, and deep breathing.

Strategies to Protect NAD+ from Stress: Optimizing Lifestyle
Beyond direct stress reduction, overall lifestyle significantly influences NAD+ levels and their resilience to stressors. A balanced diet is foundational for cellular health and optimal NAD+ metabolism. A diet rich in whole foods—fresh fruits, vegetables, lean proteins, and healthy fats—provides essential vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants that support mitochondrial function and protect against oxidative stress. Foods containing NAD+ precursors, like niacin (vitamin B3) in forms such as nicotinamide riboside (NR) and nicotinamide mononucleotide (NMN), can directly help increase NAD+ levels, lessening the impact of stress on NAD+ levels.
Regular physical activity is another powerful tool for maintaining NAD+ health. Moderate exercise stimulates mitochondrial biogenesis—the creation of new mitochondria—and improves the efficiency of existing ones. This enhances NAD+ production and its utilization in cellular processes. Exercise also effectively manages stress by releasing endorphins and lowering cortisol. Finally, sufficient, quality sleep is crucial for body restoration and regulating biochemical processes, including NAD+ metabolism. Chronic sleep deprivation is a powerful stressor that can significantly reduce NAD+ levels, whereas adequate sleep supports its restoration, mitigating the impact of stress on NAD+ levels.
- Ensure sufficient, quality sleep for NAD+ restoration.
- Maintain a balanced diet rich in whole foods and NAD+ precursors.
- Engage in regular moderate physical activity to support mitochondrial health.
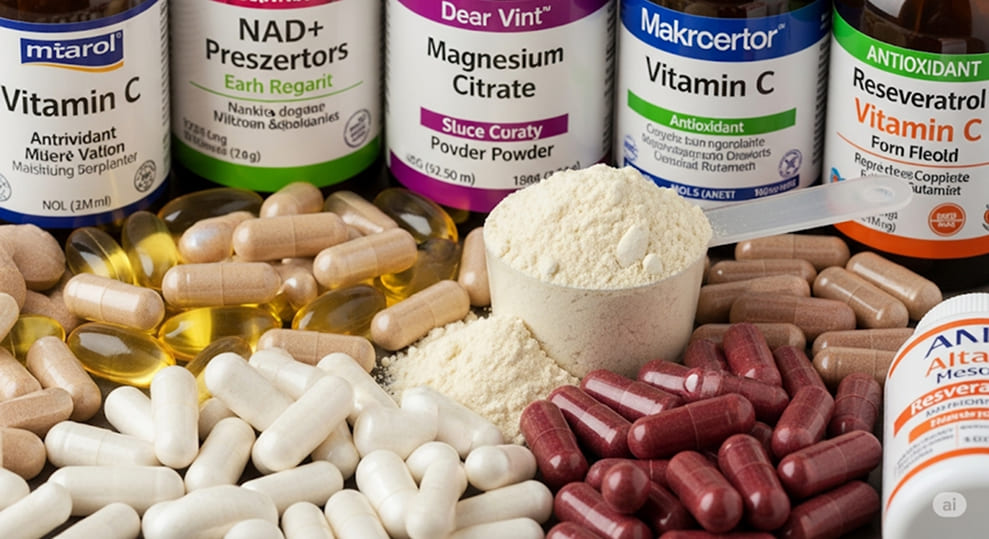

Supporting NAD+ Levels with Nutrients and Supplements
Beyond general lifestyle recommendations, specific nutrients and dietary supplements can directly support and protect NAD+ levels under stress. A well-known NAD+ precursor is niacin (vitamin B3), available as nicotinamide, nicotinic acid, and importantly, nicotinamide riboside (NR) and nicotinamide mononucleotide (NMN). Research indicates NR and NMN are particularly effective for increasing cellular NAD+ levels, as they are readily absorbed and utilized for its synthesis. Supplementing with these can help replenish NAD+ stores, which are depleted by stress, thereby countering the impact of stress on NAD+ levels.
Other nutrients also play vital roles. Magnesium is a cofactor for many enzymes involved in NAD+ metabolism; its deficiency can negatively affect NAD+ production. Resveratrol, a potent antioxidant found in red wine and berries, activates sirtuins, which utilize NAD+. PQQ (pyrroloquinoline quinone) is another compound that supports mitochondrial function and may boost NAD+ levels. Always consult a healthcare professional before taking any supplements, especially if you have chronic conditions or are on medication, to ensure safety and appropriateness. This careful approach helps manage the impact of stress on NAD+ levels.
- Explore supplements supporting mitochondrial function, such as PQQ and antioxidants like resveratrol.
- Consider NAD+ precursor supplements like nicotinamide riboside (NR) or nicotinamide mononucleotide (NMN).
- Ensure adequate magnesium intake, essential for NAD+ metabolism.

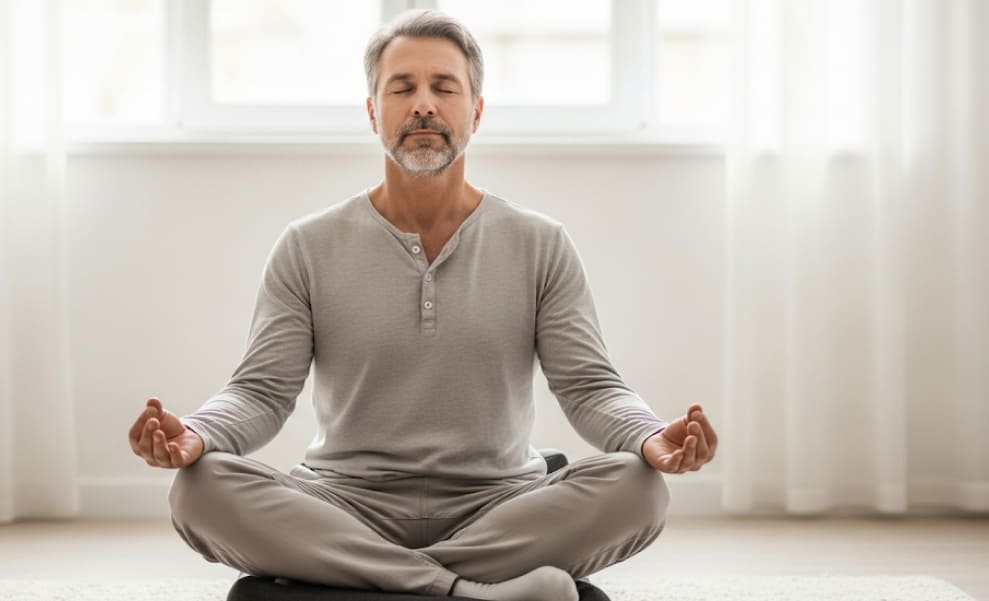
The Impact of Meditation and Mindfulness on Cellular Health
Meditation and mindfulness practices, beyond their direct stress-reducing effects, profoundly influence cellular processes, including those linked to NAD+ levels. These practices alter brain activity, reduce stress hormone production, and activate the parasympathetic nervous system, responsible for relaxation and restoration. Regular meditation is believed to contribute to increased telomere length—protective caps on chromosomes that shorten with cell division and are markers of biological aging. Protecting telomeres is indirectly associated with maintaining cellular health and, consequently, optimal NAD+ levels, thus moderating the impact of stress on NAD+ levels.
Furthermore, meditation and mindfulness can influence gene expression, regulating sirtuin activity. Sirtuins, as mentioned, are NAD+-dependent proteins crucial for cellular longevity and stress resilience. Studies suggest mindfulness practices can enhance sirtuin activity, optimizing NAD+ utilization and boosting cellular protection. Regular meditation also reduces inflammation, another factor that depletes NAD+. Thus, incorporating meditation or mindfulness into your routine is not just about improving emotional well-being but also a powerful tool for profound cellular health support, mitigating the impact of stress on NAD+ levels.
- Practice meditation and mindfulness to lower stress hormones and activate parasympathetic response.
- Utilize these practices for potential telomere protection and cellular longevity.
- Mindfulness can boost sirtuin activity, optimizing NAD+ utilization.

Long-Term Perspectives and a Holistic Approach to NAD+ Protection
Protecting NAD+ levels from the adverse effects of stress is not a one-time fix but a comprehensive, long-term process requiring a consistent and conscious approach. It’s crucial to understand that no single strategy is a panacea. The most effective method is a combination of all the aforementioned approaches: active stress management, lifestyle optimization, targeted nutrient support, and practices like meditation. This synergistic approach creates optimal conditions for maintaining high NAD+ levels and, consequently, overall health and well-being, effectively addressing the impact of stress on NAD+ levels.
When implementing these strategies, patience and consistency are key. Results may not be immediate, but over time, a holistic approach will yield tangible benefits. Regular self-assessment, consulting with biohacking or healthcare professionals when necessary, and adjusting strategies will allow for maximum personalization. Ultimately, actively protecting NAD+ levels is an investment in longevity, energy, and resilience to the challenges of the modern world, enabling one not just to survive but to thrive amidst stress, lessening the impact of stress on NAD+ levels.
- Employ a holistic approach combining stress reduction, healthy lifestyle, nutritional support, and meditation.
- Be patient and consistent, as long-term results require time.
- Regularly assess your condition and consult specialists for tailored strategies.
Frequently Asked Questions about The Impact of Stress on NAD+ Levels
OPEN
How does stress directly affect NAD levels?
Stress triggers the release of hormones like cortisol and activates enzymes like PARP. Cortisol increases the consumption of NAD+, while PARP enzymes, crucial for DNA repair (which is heightened during stress), also utilize significant amounts of NAD+. This increased demand, coupled with potential mitochondrial dysfunction caused by chronic stress, leads to a depletion of your body’s NAD+ reserves.
Can lifestyle changes truly make a difference in protecting NAD+ from stress?
Absolutely. Lifestyle optimization is a cornerstone of protecting NAD+ levels. A balanced diet rich in NAD+ precursors and antioxidants, regular moderate exercise to boost mitochondrial function, and sufficient, quality sleep for cellular repair are all vital. These habits work synergistically to reduce the overall burden of stress on your system and support NAD+ regeneration.
What specific nutrients or supplements are most effective for supporting NAD+ levels under stress?
Key nutrients include niacin (Vitamin B3) in its highly bioavailable forms like Nicotinamide Riboside (NR) and Nicotinamide Mononucleotide (NMN), which directly serve as precursors for NAD+ synthesis. Magnesium is also important as a cofactor in NAD+ metabolism. Additionally, powerful antioxidants like resveratrol and PQQ can help protect cells from oxidative stress, thereby indirectly safeguarding NAD+ levels. Always consult a healthcare professional before starting any new supplement regimen.
How do mindfulness and meditation specifically influence NAD+?
Beyond general stress reduction, mindfulness and meditation profoundly impact cellular processes. They can reduce stress hormone production and activate the parasympathetic nervous system, promoting relaxation and cellular repair. Research suggests these practices might influence gene expression, potentially enhancing the activity of sirtuins—NAD+-dependent proteins crucial for cellular longevity and resilience. By lowering inflammation, they also prevent another factor that depletes NAD+.
Is protecting NAD+ a short-term fix or a long-term commitment?
Protecting NAD+ from the impact of stress on NAD+ levels is very much a long-term, ongoing commitment rather than a quick fix. It requires a holistic and consistent approach, integrating stress management techniques, a healthy lifestyle, targeted nutritional support, and mindfulness practices. The benefits, such as increased energy, enhanced longevity, and greater resilience to life’s challenges, accumulate over time with sustained effort.